This week, I have been continue to work on my second brief. I have come to a bit of a stand still with this project. I came up with an idea to show off my process that doesn’t feel like me and I am trying to figure out what on earth I am going to do and see how I can develop the design or what I can do to replace it. I have been trying to interact with canvas and see if any of the lectures or reading material sparks some form of inspiration for my amendments
This weeks lecture notes
- How do you approach research methodologies for your academic journey?
- My definition of what research is:
- The process of finding thoughts and ideas from past or recent professionals to help spark the idea of imagination and investigation.
- Etymology – the study of words, their origin and how their form and meaning have changed over time.
- Research – come from the French word meaning ‘to closely search
- Also derives from the Latin word Socar – to closely wander. We are constantly seeking, searching. Wandering through material.
- Philosophy
- Human knowledge comes from the idea of experience and the questioning of the experience through reflective process.
- Philosophy is the study of the fundamental nature of knowledge, reality and existence.
- Rationalists claimed the ultimate starting point of knowledge is reasoning.
- Rationalism – in it’s purest form believes all rational beliefs and human knowledge comes from innate principles and first concepts
- Empiricists – sense and experience is the start of all knowledge
- Knowledge is made of 4 keys concerns: – metaphysics, aesthetics, ethics and epistemology.
- Metaphysics
- Asks questions about reality
- Looks into ontology- the nature of being.
- Asks the big questions. Man, God. The truth behind it all?
- Aesthetics
- Questions of beauty
- Deals with judgement and perception. Order and proportion
- Ethics
- How we should conduct ourselves.
- Questions of morality, judgement, the relationship between the individual and the state.
- Epistemology
- Theory of knowledge itself
- Questions of its origin, methods, validity, limits and scope, justified belief vs opinion.
- Metaphysics
- Methodology
- A branch of knowledge that deals with the general principles or axioms of the generations of knowledge.
- Refers to the rationale and philosophical assumptions of natural, human science study.
- It’s the pillar of knowledge you stand on.
- Methodologies describe the approach you are taking.
- Methods
- The way you collect data and information for analysis, enquiries and decision making.
- It’s the different techniques that you use to find sources.
- Qualitative – looks into discourse and language
- Quantitive – looks into data and analysis
- Primary source – first hand account and whiteness to subject
- Secondary source – something that was created after the event and did not see it first hand
- Ethnography
- Research approach that produces a detailed in-depth observation of people’s behaviour, beliefs and preferences by observing and interacting with them in a natural environment.
- Visual research : an introduction to research methods in graphic design – Ian Noble & Russel Bestley
- Pure research- the investigation of graphic and visual languages in a propositional sense, rather than those that have a predetermined commercial application.
- Applied research – the investigation of a practical problem usually with the underlying intention of creating potential practical solutions.
- Deductive research – research that starts from the position of a general conclusion and then searches for data to support it.
- Empirical research – investigation into a field of study that is based on direct observation of phenomena.
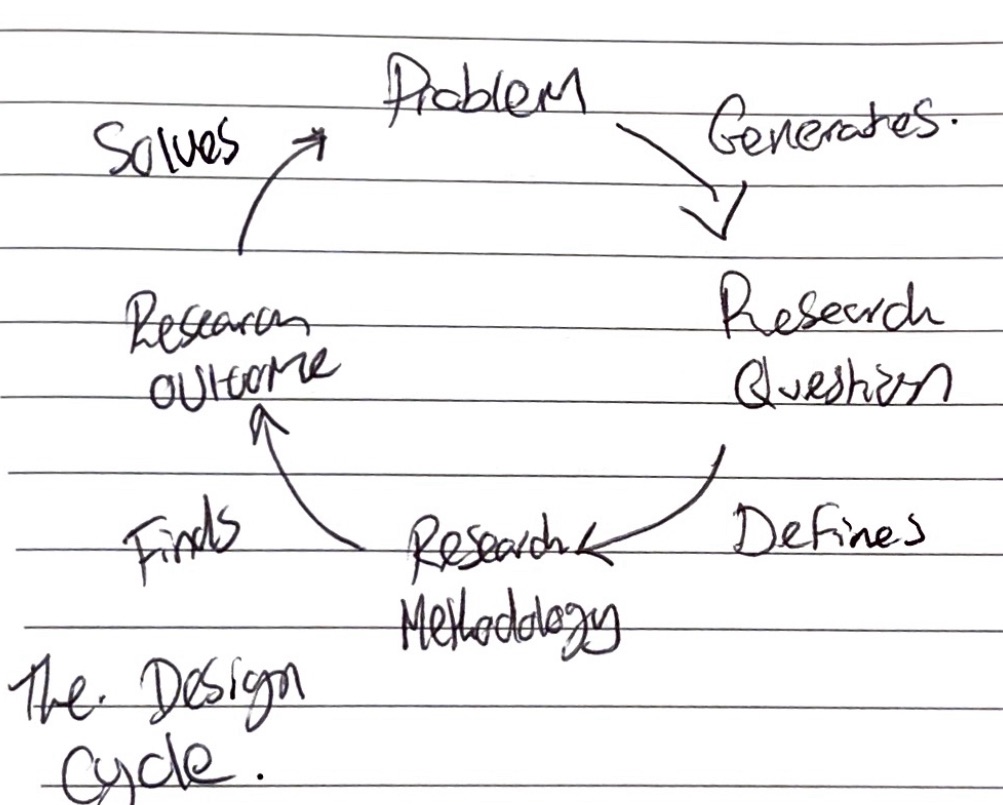
- The design cycle
Leave a comment